Intel®’s Trust Domain Extensions (TDX) is Intel’s most recent addition to its portfolio of Confidential Computing technologies, which also includes Intel® Trust Authority and Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX).
Intel® TDX plays a crucial role in the Confidential Computing Initiative, which aims to enhance data security and privacy by protecting sensitive workloads and data during processing, a traditionally vulnerable stage of the data lifecycle. It creates a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) within hardware that isolates and secures computations from the broader system, including the operating system, hypervisor, and potentially malicious actors. This initiative is particularly relevant for cloud computing, where multiple tenants share the same infrastructure, as it ensures that data remains confidential even when processed on third-party platforms.
What is Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (TDX)?
Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (TDX) is a unique hardware-based technology designed to enhance the security and privacy of virtualized workloads in cloud environments. It achieves this through the use of Trust Domains (TDs), which are isolated virtualized environments for securely running sensitive applications and data, even in potentially hostile environments, such as shared multi-tenant cloud infrastructures.
TDX isolates entire virtual machines(VMs) from the underlying physical hardware and infrastructure, including the operating system, hypervisor, and other VMs running on the same hardware. This isolated virtual environment called the Trust Domain (TD) is the core component of how TDX operates.
TDX became more widely available with Intel’s 4th Generation Xeon Scalable Processors (Sapphire Rapids), starting in early 2023. TDX represents a significant leap in terms of how confidential computing is implemented and what it aims to protect.
Core Components of Intel® TDX
The TDX solution is built using a combination of Intel® Virtual Machine Extensions (VMX) and Multi-Key Total Memory Encryption (MK-TME), as extended by the Intel® Trust Domain Extensions Instruction Set Architecture (Intel TDX ISA). The Intel TDX software module is designed to implement the TDX architecture. The platform is managed by a TDX-aware host Virtual Machine Manager (VMM). The VMM can launch and manage both guest Trust Domains (TDs) and legacy guest VMs. From the perspective of legacy VMs, all functionality remains unchanged, while the VMM is restricted only in how it manages the TDs, ensuring their security and isolation.
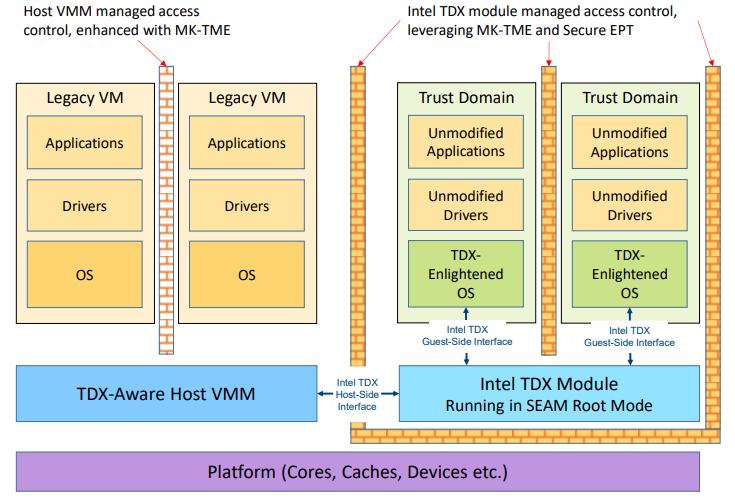
The above image is copyright Intel® and has been sourced from their documentation here.
TDX incorporates several hardware and software components to achieve its security objectives. These components include:
- Trust Domain (TD) – A Trust Domain is a secure, isolated execution environment (enclave) where the virtual machine’s code and data are protected. The TD is isolated not only from the host operating system and hypervisor but also from other TDs running on the same hardware. This type of isolation make sure that the contents of a TD remain confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
- TDX Module – The TDX Module is a trusted component responsible for managing the creation and maintenance of Trust Domains. The module operates with reduced privileges. Also it isolated from both the virtual machines and the hypervisor, thus ensuring that it cannot interfere with the execution of the Trust Domains. It handles tasks such as TD initialization, state management, and communications with other system components.
- Memory Encryption – TDX relies on hardware-based memory encryption to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data stored in memory. If a malicious actor happens to gain access to the physical memory, by encrypting the contents of a TD, the system ensures that they cannot read or modify the encrypted data.
- Remote Attestation – TDX supports remote attestation, which allows an external party to verify the integrity of the system and its software stack before interacting with a TD. This process involves the generation of cryptographic evidence that can be used to prove that the TD is running on a trusted platform and that its software has not been tampered with.
- Measured Boot – Measured boot is another key feature of Intel® TDX. During system boot, cryptographic measurements of the software stack are recorded in secure storage. This helps to verify that the system has booted into a known and trusted state, and provides assurance that the platform has not been compromised.
Intel® TDX 1.5 (released in December 2023) introduced several new features aimed at enhancing flexibility and security in confidential computing environments:
- Live Migration – A running Trust Domain (TD) can be migrated from one platform to another without disrupting the workload.
- TD Preserving – An existing TD can continue running even after a TDX module update, avoiding the need to restart the workload.
- vTPM Support – This feature provides a virtual Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0, enhancing attestation and encryption for TDs.
Benefits of Intel® TDX
Cloud service providers, enterprise IT providers and multi-tenant systems that deal with virtualized environments benefit from the features offered by Intel® TDX.
- Enhanced Security and Isolation – TDX provides hardware-level isolation of Trust Domains(TDs) from the hypervisor, host OS, and other VMs, this significantly reducing the attack surface. This means that even if the hypervisor is compromised, sensitive data and applications running in TDs remain secure.
- Remote Attestation – Remote attestation provides a way to verify the integrity of a TD. Cloud customers running sensitive workloads need assurance that the workloads are being run in a trusted environment. This enables secure communication between the TD and external services or clients.
- Support for Virtualization – Intel® TDX is designed to work seamlessly in virtualized environments and does not require significant changes to existing virtualization infrastructure, making it an ideal solution for cloud service providers and any enterprises running virtual machine environments.
With OpenMetal, you get full root access to your hardware with Intel® TDX so you already have control over the virtualized environments for your customers. If you are a public cloud provider or a VM provider, you can even monetize this feature.

Intel® TDX is available in newer Intel processors such as the 4th and 5th generation Xeon chips. OpenMetal has enterprise hardware that incorporates these chips and is able to work with customers to enable TDX for their infrastructure. A popular option is the OpenMetal XL v4.0 with dual Intel Xeon Gold 6530 processors.
Relationship between TDX and SGX
Both Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (TDX) and Intel® Software Guard Extensions (SGX) are designed to enhance security via hardware based isolation, however they operate at different levels of the system. They can co-exist on the same computing stack, but their integration depends on the specific use case.
The most crucial difference is that while Intel® Software Guard Extensions (SGX) focuses on protecting smaller, application-specific enclaves, TDX extends the concept to isolate entire VMs, ensuring that even if the hypervisor is compromised, the contents of a TD (such as code and data) remain secure.
So SGX is more targeted and application specific, designed for smaller workloads, limited in scale and does require developers to modify application code to be able to use SGX’s secure enclaves.
And since the Trust Domain(TD) created by the TDX secures entire workloads and not just portions of applications, it is particularly suited for cloud environments and multi-tenant infrastructures, where multiple VMs share the same hardware but need to remain secure from each other.
Conclusion
Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (Intel® TDX) is a powerful technology that addresses some of the most pressing challenges around data privacy and security in cloud computing, particularly in multi-tenant environments. TDX provides enhanced protection for sensitive workloads by creating isolated, secure execution environments (Trust Domains) that protect the data and workloads from unauthorized access, even if the underlying infrastructure is compromised. Intel® TDX is essential for confidential computing and secure multi-party collaboration, particularly for industries prioritizing data security and privacy. Read more about TDX on the official Intel® site
Interested in the OpenMetal IaaS Platform?
Bare Metal Servers
High end bare metal server hosting for virtualization, big data, streaming, and much more.
Hosted Private Cloud
Day 2 ready. No licensing costs. Delivered in 45 seconds. Powered by enterprise open source tech.
Consult with Our Team
Meet our experts to get a deeper assessment and discuss your unique IaaS requirements.