Struggling with OpenStack Neutron networking issues? This guide gives you practical steps to identify and resolve common problems like connectivity failures, VLAN misconfigurations, DNS/DHCP issues, and more. Here’s what you’ll find:
- Quick fixes for basic connectivity issues using tools like
ping,traceroute, andtcpdump. - Step-by-step troubleshooting for VLAN setups, virtual routers, and Linux bridges.
- Log file locations and commands to debug Neutron components like DHCP and L3 agents.
- Security group misconfigurations explained, with easy ways to test and resolve them.
- Advanced tools like Open vSwitch (OVS) diagnostics and containerized service logs for deeper insights.
We’ll equip you with the tools and commands to keep your OpenStack network running smoothly. Let’s get into it!
Related Video: Troubleshooting Neutron Virtual Networks
Preparing to Troubleshoot
Efficient troubleshooting in OpenStack can save you a lot of time and effort.
Network Testing Tools
Command-line tools are key for diagnosing network issues. For example, the ping command is great for checking basic connectivity. It uses the ICMP protocol and is perfect for initial tests.
If you need to analyze the path that data takes, traceroute is your tool. On Unix-like systems, it uses UDP packets by default, while Windows systems (using tracert) rely on ICMP Echo Request packets.
| Tool | Primary Use | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| ping | Basic connectivity | ICMP |
| traceroute/tracert | Path analysis | UDP/ICMP |
| tcpdump | Packet analysis | All protocols |
| neutron CLI | Service management | API |
Finding Network Logs
Network logs are a goldmine for identifying problems. Neutron service logs are stored in the /var/log/neutron/ directory on their respective host machines. Each component has its own log file:
| Component | Log Location |
|---|---|
| DHCP Agent | /var/log/neutron/dhcp-agent.log |
| L3 Agent | /var/log/neutron/l3-agent.log |
| Server | /var/log/neutron/server.log |
| Metadata Agent | /var/log/neutron/metadata-agent.log |
To troubleshoot effectively, correlate timestamps across these logs to identify patterns or issues.
Network Components
OpenStack networking relies on several key services working together. The neutron-server handles API requests and database access, usually running on controller nodes. Meanwhile, Layer 2 (L2) and Layer 3 (L3) agents manage network segmentation and routing, respectively.
You can check the status of these components with this command:
openstack network agent list
This will show all network agents and their current status. Make sure all agents are active and configured correctly for your chosen network plugin.
Armed with these tools and insights, you’re ready to tackle connection issues in the next section.
Fixing Connection Problems
When OpenStack Neutron encounters network issues, a structured approach can help pinpoint and resolve connectivity problems. This guide walks you through testing connectivity, checking VLAN setups, and addressing DNS/DHCP issues step by step.
Testing Basic Connectivity
Start by using ping to test connectivity at critical network points. This helps narrow down where the issue might be.
| Test Target | What It Reveals | Next Steps If Failed |
|---|---|---|
| Internet | External connectivity | Check if other machines can access the internet. |
| Physical Router | Local gateway issues | Inspect the router or switch status. |
| Neutron Router | OpenStack networking | Look into the L3 agent logs. |
| Other Instances | Internal networking | Check the virtual switching configuration. |
To find the relevant namespace:
ip netns list
To capture ICMP traffic for troubleshooting:
ip netns exec qrouter-62ed467e-abae-4ab4-87f4-13a9937fbd6b tcpdump -qnntpi any icmp
If these tests pass, move on to verifying VLAN configurations.
VLAN and Network Setup
Here are key areas to inspect when dealing with VLAN and network setup issues:
- Bridge Interface Flow: Use this command to inspect flows on the bridge interface:
ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-ex - L3 Agent Configuration: Check the
/etc/neutron/l3_agent.inifile to ensure theexternal_network_bridgevalue is not empty. - VLAN Ranges: Confirm the tenant network VLAN IDs in
/etc/neutron/plugin.ini.
To create a VLAN provider network, you can use these commands:
neutron net-create provider --provider:network_type=vlan --provider:physical_network=phy-eno1 --provider:segmentation_id=120
neutron subnet-create "provider" --allocation-pool start=192.168.120.1,end=192.168.120.253 --disable-dhcp --gateway 192.168.120.254 192.168.120.0/24
Once the VLAN setup is confirmed, focus on DNS and DHCP configurations.
DNS and DHCP Solutions
Problems with DNS or DHCP can prevent instances from being configured correctly. Follow these steps to troubleshoot:
- Check the DHCP Agent Status:
neutron agent-list - Use dhcpdump in the DHCP namespace to monitor DHCP traffic during instance startup.
- Set Up DNS Resolution:
openstack subnet set --dns-nameserver 8.8.8.8 flat-subnetAdd the following settings to
/etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.ini:dnsmasq_dns_servers = 8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4 dnsmasq_local_resolv = true
Finally, check for errors in the DHCP logs located at /var/log/neutron/dhcp-agent.log.
sbb-itb-f4461f5
Virtual Network Repairs
Once you’ve tackled basic connection problems, it’s time to focus on the virtual network components to wrap up your troubleshooting process.
Open vSwitch (OVS) Fixes
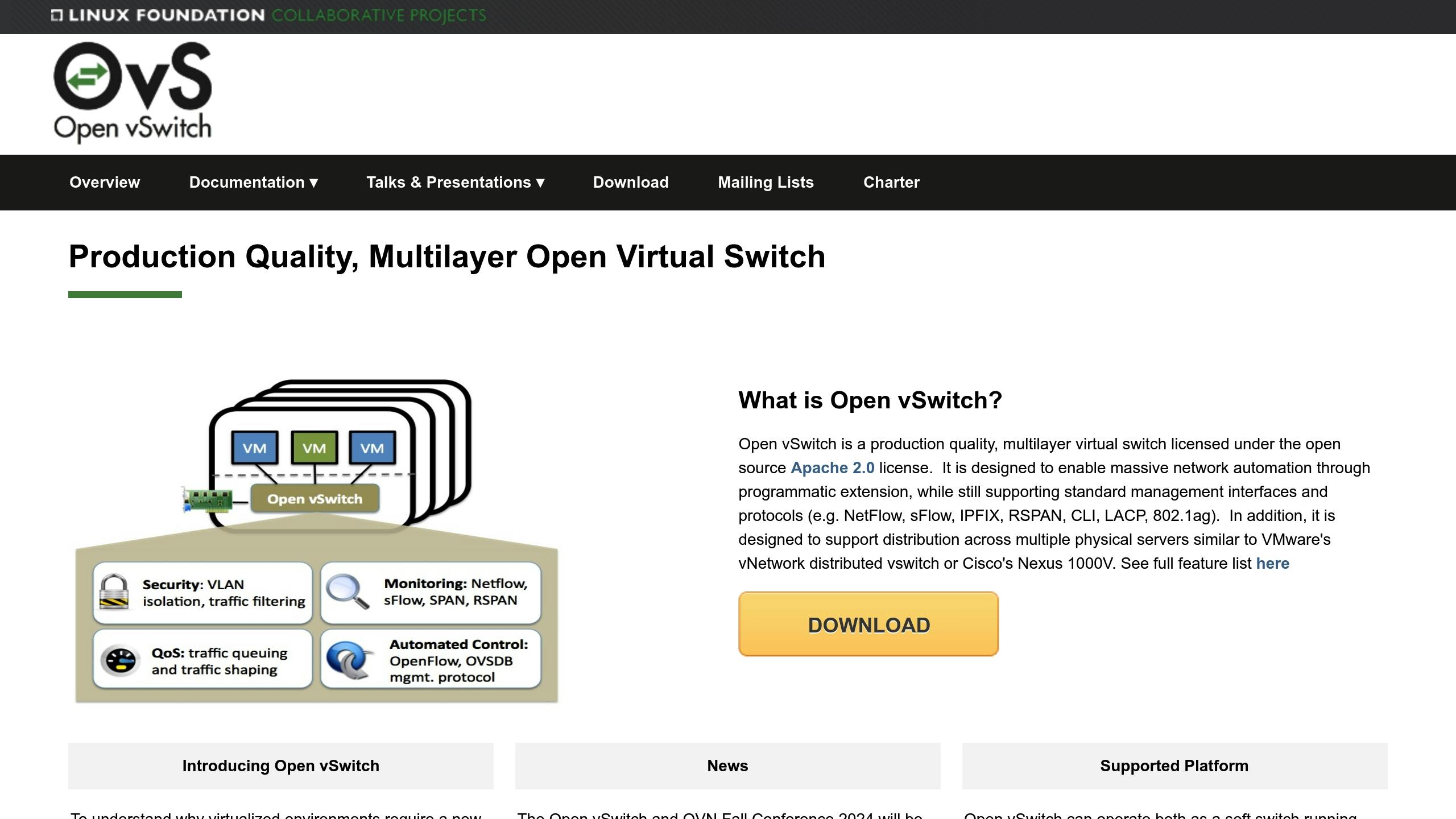
Here are some commands to help pinpoint and resolve OVS issues:
# Get an overview of the database configuration
ovs-vsctl show
# Display OpenFlow table entries
ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int
# Inspect datapath flows
ovs-dpctl dump-flows
Typical OVS issues and how to address them:
| Problem | Diagnostic Command | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Missing Ports | ovs-vsctl list-ports br-int | Add back missing ports using ovs-vsctl add-port |
| Flow Table Errors | ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int | Clear and reinitialize flows with ovs-ofctl del-flows |
| Connectivity Problems | ovs-appctl bridge/dumpflows br-int | Check port settings and ensure direct connectivity |
Linux Bridge Solutions
Linux bridge problems often arise when the agent appears ‘admin up’ but isn’t functioning. Start by reviewing the configurations:
brctl show br-mgmt
ip address show dev br-mgmt
Double-check the bridge agent settings in /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/linuxbridge_agent.ini:
[linux_bridge]
physical_interface_mappings = provider:eth1
To confirm VLAN connectivity, use:
ip link show | grep eth1
tcpdump -i eth1 -n vlan
Ensure these configurations are accurate to keep the virtual network running smoothly.
Virtual Router Fixes
Issues with virtual routers can interrupt tenant connectivity. Use the following commands to diagnose and resolve problems:
# List router namespaces and test connectivity
ip netns list | grep qrouter
ip netns exec qrouter-<ID> ping 8.8.8.8
# Check SNAT rules
ip netns exec qrouter-<ID> iptables -t nat -L -n -v
When adjustments are needed, follow these steps:
openstack router show <router_name>
neutron router-port-list <router_id>
neutron router-gateway-clear <router_id>
neutron router-gateway-set <router_id> <external_network_id>
Security Group Problems
Security group misconfigurations can block connectivity. Here’s how to identify and resolve these issues.
Finding Security Group Errors
OpenStack’s default security group settings are intentionally restrictive, which can block connectivity for new instances. To troubleshoot:
# List security groups and their rules
openstack security group list
openstack security group rule list default
# Check instance security group assignments
openstack server show <instance_id>
Some common issues include:
| Problem | Symptom | How to Check |
|---|---|---|
| Asymmetric Rules | Outbound traffic works, inbound fails | `iptables-save |
| Missing ICMP Rules | Ping requests fail | `openstack security group rule list default |
| Incorrect Port Range | Application timeouts occur | `neutron security-group-rule-list |
If these steps don’t solve the problem, check for potential firewall conflicts.
Fixing Firewall Conflicts
Conflicts between Open vSwitch (OVS) and iptables can disrupt security group rules. To troubleshoot:
# Check the firewall driver in use
grep -i firewall_driver /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/openvswitch_agent.ini
Here are some key differences to keep in mind:
- OVS blocks INVALID connection states, while iptables may allow them if they match security group rules.
- Multicast traffic (224.0.0.X) passes through OVS by default but requires explicit rules in iptables.
- Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) rules can override security group settings.
Testing Security Changes
After adjusting security groups, always test the changes:
# Create a test security group
openstack security group create test_group --description "test group"
# Add test rules
openstack security group rule create test_group \
--protocol tcp \
--dst-port 22:22 \
--remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
“Security groups are sets of IP filter rules that are applied to all project instances, which define networking access to the instance.” – OpenStack Docs
Follow these steps to confirm everything is working:
- Check rule propagation: Ensure iptables reflects the new rules.
- Test connectivity: Verify ICMP traffic passes through.
- Validate port access: Confirm specific ports, like SSH, are accessible.
- Confirm bidirectional flow: Ensure traffic flows both ways without issues.
Once testing is complete, clean up the test security group:
# Delete the test security group
openstack security group delete test_group
Finally, verify overall network connectivity to confirm the changes are effective.
OpenMetal Network Solutions
OpenMetal provides integrated tools to simplify network troubleshooting, building on standard Neutron capabilities with improved logging and container-based setups.
OpenMetal Cloud Features
The OpenStack-powered infrastructure from OpenMetal offers tools for handling network issues. By using Kolla Ansible, OpenStack services are deployed in Docker containers, making network management more efficient. All network logs are centralized in /var/log/kolla/<service-name>, allowing for faster problem solving.
For advanced log management, OpenMetal supports integration with the Elasticsearch and Kibana (ELK) stack, offering:
| Feature | Benefit | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Log Aggregation | Centralized view of all network events | Automatically collects logs from services |
| Visual Analytics | Interactive dashboards for monitoring | Powered by Kibana visualizations |
| Search Capabilities | Quickly find network issues | Full-text search across logs |
Network Management with OpenMetal
OpenMetal enhances troubleshooting by leveraging OpenStack Neutron’s Network-as-a-Service features. It integrates with OpenStack’s tools to improve network diagnostics.
Administrators can use commands like these to investigate network issues:
docker logs neutron_server
less /var/log/kolla/neutron/server.log
This centralized logging system helps pinpoint common problems:
| Issue Type | Log Location | Key Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Failures | neutron-server logs | Error codes, stack traces |
| DHCP Problems | neutron-dhcp-agent logs | IP allocation failures |
| Router Issues | neutron-l3-agent logs | Routing table errors |
Additionally, OpenMetal’s integration with Ceph ensures dependable storage networking, while its containerized services allow updates without service interruptions.
Wrapping Up: Troubleshooting Neutron Networking in OpenStack
This section outlines troubleshooting steps and maintenance practices for networking issues, combining established methods with OpenMetal’s advanced solutions. Use this guide to ensure your network stays reliable and efficient!
Quick Reference Guide
Follow these steps to troubleshoot Neutron networking issues effectively:
| Issue Type | Basic Tests | Advanced Troubleshooting | Key Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Connectivity | Use ping to test connectivity between internet, router, and VMs | Run tcpdump at critical points | Check service status; restart if needed |
| VLAN Setup | Ping the gateway IP | Inspect flow and configuration | Confirm VLAN ranges |
| Namespace Issues | Identify the network namespace | Use ip netns exec commands | Verify namespace setup |
| DNS/DHCP | Check the dnsmasq process | Test hostname resolution | Restart the DHCP agent |
| OVS Problems | Confirm OVS bridges | Inspect port connections | Ensure correct bridge configuration |
These steps address common issues, but ongoing maintenance is of course required for long-term network stability.
Network Maintenance Tips
Keep your network in top shape with these practices:
- Service Monitoring
- Use automated tools to track OpenStack services.
- Set up alerts for critical metrics to catch issues early.
- Early detection helps minimize downtime.
- Regular Updates
- Update OpenStack components on a consistent schedule.
- Keep a centralized log of Neutron changes for easy reference.
- Automated Diagnostics
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Service Status Check | Daily | Spot agent issues early |
| Log Analysis | Weekly | Identify recurring problems |
| Configuration Backup | Monthly | Simplify recovery processes |
| Security Group Audit | Quarterly | Avoid connectivity disruptions |
Read More on the OpenMetal Blog



































