In today’s world, the vast majority of organizations have adopted either a public cloud or private cloud, however, within these organizations, their IT professionals face the challenge of determining the best ROI with placement of their dollars against cloud services provided by either public clouds or private clouds.
There’s no provider that guarantees the best ROI across the board. The best provider for your workload will depend on your workload size, requirements, expertise of your in house technical team, budget, etc. In this blog we will explore various cloud solutions and what workloads they may be best suited for.
Public Cloud
Public cloud providers like AWS and GCP allow users to get started on the cloud without heavy investment in hardware. If you’re using a public cloud provider and your cloud bill is under $10,000 per year, then you’re probably using the best-suited cloud type for your needs. So switching may not be worth the time and effort, but there are some things you can do to reduce your infrastructure costs on public cloud.
FinOps practices to reduce public cloud costs:
Understand Your Cloud Bill
The first step to controlling your bill is understanding what your high cost areas are. Public clouds bills can be difficult to navigate with all the variables. Pricing varies by instance type, usage, bandwidth usage, location of the data center, and the ease of usage makes it easy for users to over-consume resources and face runover bills. All these make it difficult to predict and control your infrastructure costs if you cannot navigate the bills systems of your cloud provider.
Identify Wasted Resources (Idle and Unutilized)
Servers provisioned for temporary workloads need to be deprovisioned after use. Additionally, the attached storage needs to be deleted as well – it’s not automatically deleted when the server is deprovisioned. Temporary resources are typically provisioned at on-demand rates, which are elevated, and these charges persist until the resources are deprovisioned. With the pay-as-you-go structure, it’s imperative to keep your infrastructure lean and delete resources that are no longer necessary.
Set Budgets
It is important for engineering leaders and other executives to come together and set a budget based on project requirements and available financial resources that can be invested into a project. Most providers have a budget system in place, but some are more complicated than others to navigate. Budgets should be clearly communicated with teams and everyone needs access to real time data on expenses to avoid situations where users are blindsided when their budgets run out.
Right-Size Your Resources and Auto Scale When Needed
It’s not uncommon to have resources that need to change size to accommodate spikes. It may be tempting to leave the instances larger to avoid tedious scaling up and down but there are right-size services that can help you automate the process of scaling your instances up and down and help you avoid paying for idle resources.
Save With Reserved and Spot Instances
On-demand instances are flexible and highly available, but they come with a significant premium that can easily inflate your infrastructure bill. Reserved and spot instances provide you with instances at significantly lower prices. For example, If you had 68 E2 Medium with 9,000 GiB of Egress and 40 GiB zonal SSD in a Virginia data center from GCP, the monthly on-demand cost to your organization would be $3,147 per month. You can save 33% and reduce your monthly bill to $2,117 by switching to a 3 year termed contract with GCP. However, with the same workload, you can have a 69% expense reduction if you switch from monthly on-demand billing to a 3 year termed contract with a hosted private cloud from OpenMetal.
It may be difficult to plan your need for unpredictable workloads well in advance for reserved instances, and spot instances run the risk of disruption that may be too much of a hassle for the savings. However, some cloud providers like OpenMetal extend fair advance notice to users of spot instances. This makes these instances a practical choice for temporary and unpredictable workloads. If the instance need persists, transitioning to a reserved instance is a seamless option.
Monitor Your Cloud Usage (Cloud Monitoring Tools)
Monitoring cloud usage with cloud monitoring tools can help your businesses optimize your operational costs and ensure efficient resource utilization. Cloud monitoring tools provide real-time insights into various aspects of cloud performance, such as server load, network traffic, and storage usage. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks, forecast capacity needs, and pinpoint opportunities for optimization. Additionally, cloud monitoring tools facilitate the detection of any abnormal activities or security threats, enhancing overall system integrity.
Now if your cloud bill is over $30,000, it may be time for you to consider switching to a private cloud model. Bulk purchasing an entire cloud vs buying many VMs at high costs can reduce your cloud bill by 60+%. Learn More.
Private Cloud
If your organization has an on-premise solution it would be costly and difficult to switch. The large investment in hardware makes it difficult to ditch your on-premise solutions, but in a world of options this does not mean you are stuck. Rather than expanding your data centers, it may be cost effective to put new or temporary workloads on public or hosted private clouds. With private clouds, the bulk of costs are upfront and prepaid, therefore, the strategy to maximize the ROI of a private cloud investment differs vastly from public cloud FinOps tools. With the private cloud model, the expense is fixed, therefore the the best method for maximizing ROI is to optimize your cloud usage.
Resource Optimization
It is common practice for developers or administrators to provision temporary VMs to accommodate workloads. However, it is also common that these temporary servers, including associated storage, are not deprovisioned after the task is complete. Additionally, some VM instances may be larger than necessary to accommodate the anticipation of usage spikes. These idle or oversized VMs consume resources that could be reallocated to other projects. By implementing techniques such as right-sizing, scheduling, and autoscaling, resource utilization can be optimized thereby reducing overall costs.
Cost Allocation and Chargeback
It can be tempting to utilize all resources you have at your disposal, after all you paid for it. However, without accountability and a clear cost ownership, resources can be left idle and seem unavailable when needed by other departments leading to additional resource purchases. To realize the full benefit of your cloud spend it is important for organizations to employ clear cost allocation models to accurately track and attribute costs to specific departments or projects. Additionally, you may want to consider using chargeback models to encourage responsible resource usage and cost awareness.
Monitor Your Cloud Resource Usage
Monitoring cloud usage with cloud monitoring tools can help businesses optimize operational costs and ensure efficient resource utilization. Cloud monitoring tools provide real-time insights into various aspects of cloud performance, such as server load, network traffic, and storage usage. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks, forecast capacity needs, and pinpoint opportunities for optimization. Additionally, cloud monitoring tools facilitate the detection of any abnormal activities (that may result in unexpected billing or unauthorized spikes in bandwidth usage) or security threats, enhancing overall system integrity. With proactive monitoring, organizations can continuously review and optimize resource allocation based on their changing needs and usage patterns.
Hosted Private Cloud
Hosted private clouds bridge the private and public cloud models. With hosted private clouds, you have the best of both worlds: fixed costs, no hefty upfront costs for hardware, third party managed hardware and cloud software, root level access, and complete control of your infrastructure. Like with the private cloud model, most of your infrastructure costs will be fixed as you reserve the servers regardless of how many VMs you spin up. There will be some variable costs such as bandwidth, IPs, etc. With a hosted private cloud, to reduce your infrastructure costs, you will employ many of the same practices as you would with a traditional cloud.
But how do these models compare against each other when you look at pricing?
We took the time to layout a Key Services Map and Cost/Scale Guide for you on your quest to find the best model for your organization.
This analysis can be quite complicated, please bear with the evolution of this public cloud vs private cloud tipping point over time. To convince you of the importance, I’m jumping right into the numbers, then we’ll get back to the process.
2024 Total Monthly Cost of VM with Block Storage and Bandwidth – Public Cloud vs Managed Private Cloud Pricing
| Deployment Size, Bandwidth | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Managed Private* | Public vs Managed | Yearly Diff |
| Small – 100VMs, 10TB | $7,731 | $1,952 | $2,855 | $4,876 | $58,512 |
| Medium – 500VMs, 50TB | $28,925 | $7,375 | $11,294 | $17,631 | $211,575 |
| Large – 1000VMs, 150TB | $60,450 | $11,533 | $16,288 | $44,163 | $529,950 |
| XL – 2000VMs, 300TB | $86,260 | $18,570 | $24,775 | $61,485 | $737,820 |
| XXL – 3000VMs, 600TB | $123,061 | $25,770 | $33,788 | $89,274 | $1,071,282 |
| XXL – 4000VMs, 1200TB | $172,571 | $33,742 | $43,898 | $128,673 | $1,544,077 |
Did the numbers catch your eye? We hope so! You can calculate hosted private cloud pricing yourself using our Cloud Deployment Calculator.
Now let’s break down those numbers – at first glance, private clouds appear to be most economical solution, but let’s not forget the upfront hardware costs, data center costs, and the cost of employees to build and maintain your private cloud. If you have the in-house expertise and systems in place you may want to keep this model, but if you are switching from public cloud, the initial costs to set up a private cloud may be steep. Also scaling your infrastructure require precise planning as you will need to order hardware ahead of time. However if you are on public cloud, switching to a managed private cloud makes sense once your workload is significant enough that you can no longer ignore the dramatic savings. Once you reach the point where the difference is $200,000+ a year, it’s time to explore hosted private cloud models.
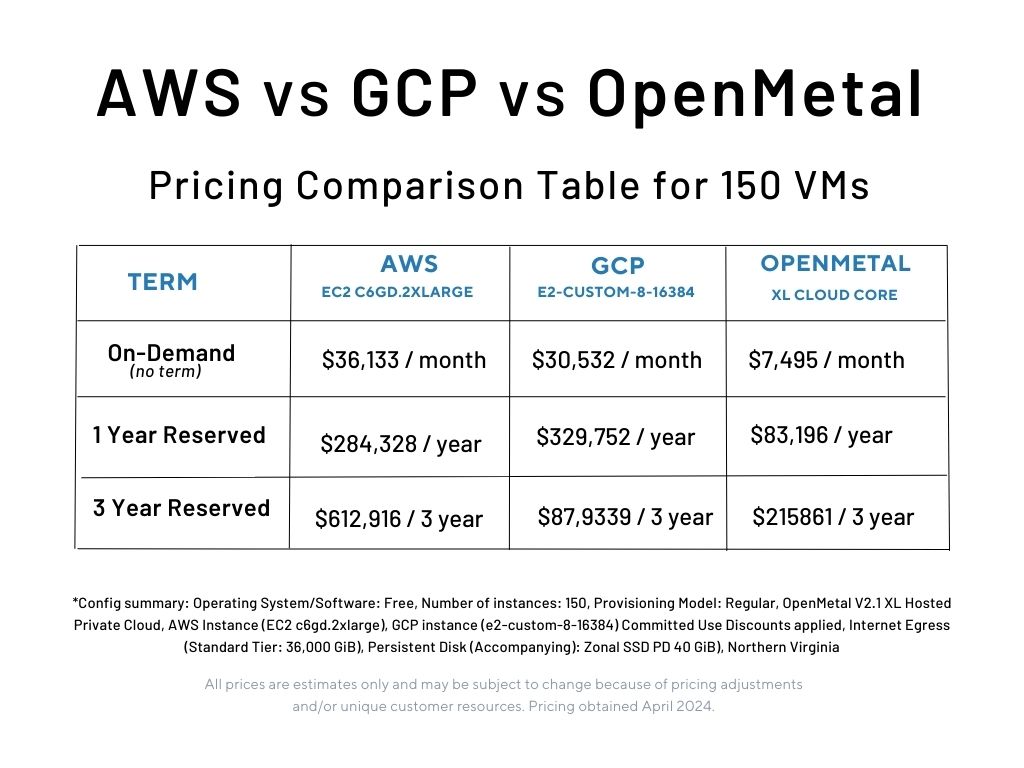
Pricing for similar resources varies dramatically across providers. Looking at the pricing data on the left, if you moved on-demand workloads on AWS to a 1 year termed contract you will save $149,268. This is quite significant savings if you’re capable of projecting your infrastructure needs for temporary workloads.
Now if you moved those workloads over to Hosted Private Clouds by OpenMetal, you would save $350,400. That’s an additional $200,000 in savings when compared to staying on AWS. Yes, having your own cloud means you would have to manage it but you can hire additional staff with the savings and take advantage of having complete root level control over your infrastructure.
Hosted Private Cloud Pricing
No building, no waiting, no hardware management. Your private cloud in 45 seconds.
AWS Alternatives
For a more detailed layout of exploring OpenMetal Cloud Cores as an alternative to AWS, visit our AWS Alternatives page. There you can look at various comparisons based on budget size, VM specs, and customer stories.
Google Cloud Alternatives
For a more detailed layout of exploring OpenMetal Cloud Cores as an alternative to GCP, visit our Google Cloud Alternatives page. There you can look at various comparisons based on budget size, VM specs, and customer stories.
Test Drive
For eligible organizations, individuals, and Open Source Partners, Private Cloud Cores are free to trial. Apply today to qualify.
Subscribe
Join our community! Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest company news, product releases, updates from partners, and more.