Cloud costs are becoming the silent killer of SaaS profit margins. If you’re managing a private equity-backed SaaS portfolio, you’ve likely witnessed this firsthand—what started as cost-effective infrastructure solutions have morphed into budget-busting line items that grow faster than revenue. The problem isn’t just the monthly bills; it’s the unpredictability, the surprise egress charges, and the realization that your infrastructure spend is eating away at the very margins that attracted investment in the first place.
The solution isn’t necessarily cutting cloud usage—it’s understanding when and how to transition from public to private cloud infrastructure. For PE-backed SaaS companies facing pressure to control costs while maintaining growth trajectories, the total cost of ownership (TCO) comparison between private and public cloud becomes critical to strategic decision-making.
What’s Driving SaaS Cloud Costs Out of Control?
SaaS companies initially embrace public cloud for good reason: instant scalability, no upfront hardware costs, and the ability to launch products quickly. But as these companies mature and their workloads stabilize, several cost drivers begin to compound.
The most significant factor is usage-based pricing unpredictability. Public cloud costs can reach 50% of total cost of revenue for software companies1, and actual spend typically exceeds committed spend by significant margins. Companies are often conservative when sizing cloud commitments due to fears of overcommitting, which means they pay premium rates for usage above their baseline.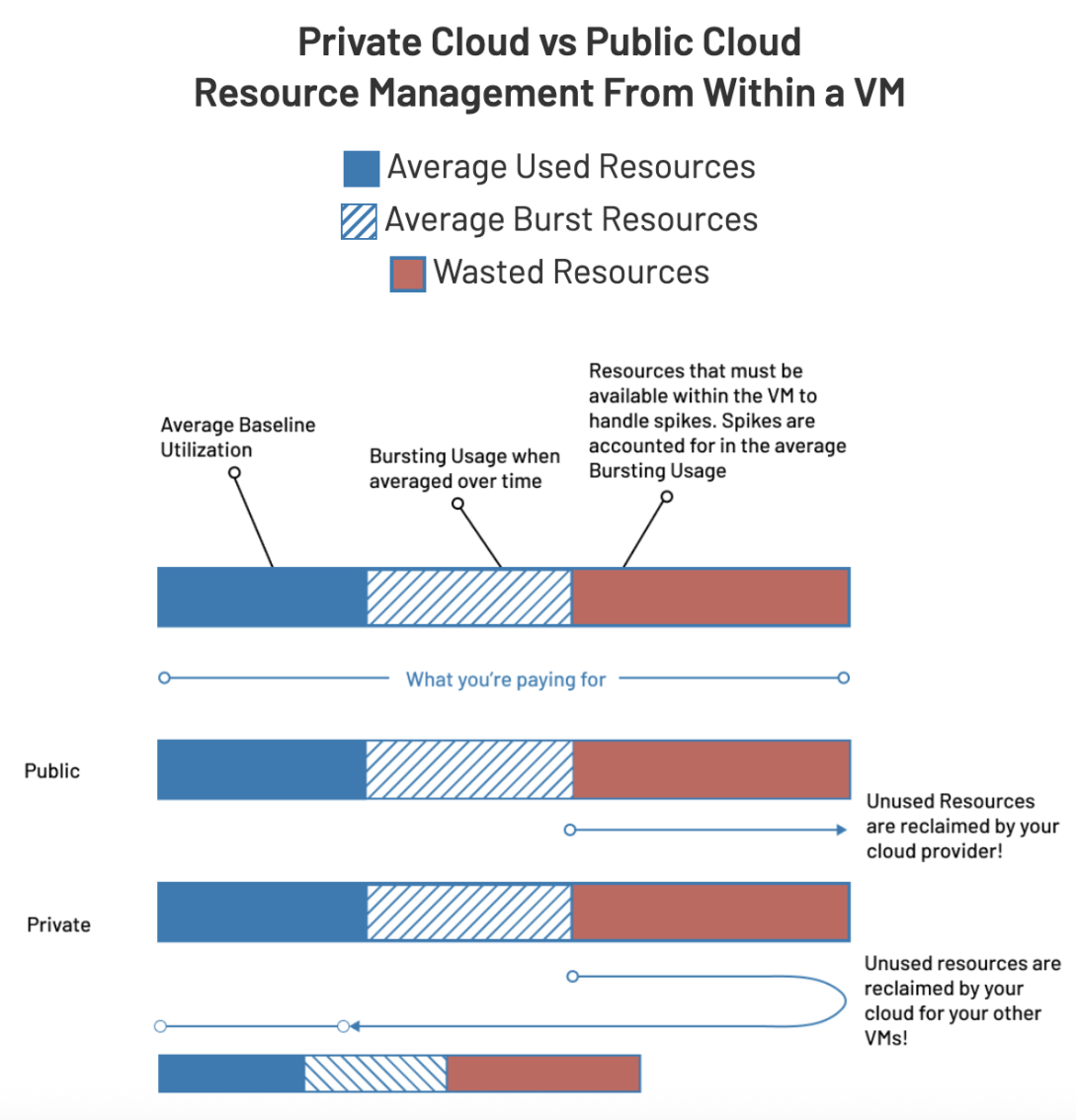
Resource inefficiency presents another major cost driver. In typical public cloud deployments, workloads use roughly 30% of allocated resources on average and burst to use no more than 30% more over time, leaving approximately 40% of VM resources wasted2. Yet you still pay for 100% of those allocated resources whether you use them or not.
Data egress fees add another layer of expense that many SaaS companies don’t fully anticipate during initial deployment. As your customer base grows and data transfer increases, these charges can become substantial portions of your monthly cloud bill.
Finally, the “instance type trap” forces SaaS companies into predetermined configurations that rarely match actual workload requirements. You pick from what hyperscalers offer, not what your applications actually need, often resulting in over-provisioned infrastructure to handle peak loads that occur infrequently.
The Private Cloud TCO Advantage for SaaS Workloads
Private cloud infrastructure can deliver significant cost advantages for SaaS companies, particularly those with predictable workloads and consistent traffic patterns. The key difference lies in resource allocation and cost structure predictability.
With OpenMetal’s private cloud approach, you lease all the resources of the physical hardware, not just virtual slices. When your VMs aren’t consuming their full allocation, those resources remain available to your other workloads within the same private environment. This eliminates the waste inherent in public cloud resource sharing models.
The cost structure becomes more predictable because there are no surprise charges for data egress or usage spikes. OpenMetal’s private clouds can be launched quickly without long-term contracts, giving SaaS companies flexibility while maintaining cost predictability. For PE-backed companies facing pressure to demonstrate consistent margins, this predictability becomes a significant strategic advantage.
Right-sizing infrastructure based on actual workload patterns rather than pre-set instance types represents one of the biggest TCO improvements. Instead of being forced into AWS or Azure’s product catalog, you configure your environment based on how your applications actually behave. This approach typically results in 30-50% cost savings compared to equivalent public cloud deployments.
Sizing Private Cloud for Different SaaS Scenarios
The infrastructure requirements for SaaS companies vary dramatically based on customer base, feature complexity, and growth trajectory. OpenMetal’s hardware configurations align with these different scenarios.
For smaller SaaS startups with moderate workloads—perhaps running web applications with a few thousand users or testing new features—a Medium V4 Private Cloud with an added Ceph storage node provides sufficient control and performance. This configuration offers enough resources to handle development, staging, and production environments without the over-provisioning common in public cloud setups.
SaaS platforms experiencing steady customer activity, handling increased data volumes, or scaling features across teams typically find XL V4 or Large V4 configurations the best fit. These provide additional storage and network flexibility suited to production environments with consistent load patterns. The predictable performance characteristics help maintain service level agreements with enterprise customers.
For compute-intensive SaaS workloads—such as real-time data processing, ETL pipelines, or encryption-heavy operations—bare metal servers with attached Ceph clusters eliminate shared VM overhead. These configurations work particularly well for platforms prioritizing performance isolation and predictability, common requirements for enterprise SaaS offerings.
The PE Perspective: Margin Compression and Value Creation
From a private equity standpoint, cloud infrastructure costs directly impact portfolio company valuations. Research from Andreessen Horowitz estimates that $100 billion of market value is being lost among the top 50 public software companies due to cloud impact on margins1.
The valuation impact becomes even more pronounced when considering how markets value gross profit improvements. High-growth software companies often trade at 24-25x gross profit multiples, meaning every dollar of gross profit saved through infrastructure optimization translates to $24-25 in market capitalization gains.
For portfolio companies with significant cloud commitments, the potential value creation through infrastructure optimization can be substantial. Dropbox’s infrastructure optimization initiative saved nearly $75 million over two years by shifting workloads from public cloud to custom-built infrastructure, with gross margins increasing from 33% to 67%1.
SaaS companies are increasingly recognizing the need to control infrastructure costs, with cloud efficiency becoming a key performance indicator. PE operating partners can drive significant value creation by helping portfolio companies evaluate their infrastructure strategies before cloud costs become prohibitive to change.
Making the Switch: Practical Considerations
Transitioning from public to private cloud requires careful planning, but the process doesn’t need to be disruptive. The key is identifying which workloads benefit most from migration and developing a phased approach.
Production workloads with predictable resource requirements represent the best candidates for initial migration. Development and staging environments can often move first, allowing teams to build familiarity with the new platform before transitioning customer-facing systems.
Data-intensive applications, such as analytics platforms or customer databases, typically see the largest cost savings from private cloud migration. These workloads often trigger significant egress charges in public cloud but operate efficiently within private cloud environments.
Applications requiring consistent performance characteristics—such as real-time processing or customer-facing APIs with strict SLA requirements—benefit from the dedicated resources and predictable latency that private cloud provides.
The migration process itself can be gradual. Rather than moving all workloads simultaneously, successful transitions often begin with a single application or environment, allowing teams to validate performance and cost savings before expanding the migration.
Cost Optimization Beyond Infrastructure
While infrastructure changes deliver immediate cost savings, the most successful SaaS companies implement comprehensive cost management practices alongside their private cloud adoption.
Making infrastructure spend a key performance indicator helps teams understand and control costs proactively. Companies like Spotify have developed internal tools that track cloud spend and enable engineers, not just finance teams, to take ownership of infrastructure costs.
Implementing incentive structures that reward cost optimization can accelerate savings. Some companies offer spot bonuses to engineers who identify and eliminate wasteful resource usage, with reported savings of millions of dollars from these programs.
Right-sizing workloads becomes easier in private cloud environments where you’re not constrained by predetermined instance types. Regular audits of resource utilization help identify opportunities for further optimization.
Architectural decisions made early in a company’s development significantly impact long-term infrastructure costs. Planning for eventual cloud optimization—including designing applications to be portable between infrastructure platforms—reduces the complexity of future cost optimization efforts.
The Economics of Scale: When Private Cloud Makes Sense
The decision between private and public cloud ultimately comes down to scale and workload characteristics. Research indicates that repatriating $100 million of annual public cloud spend typically translates to less than half that amount in total cost of ownership for equivalent private cloud infrastructure1.
For SaaS companies, the tipping point often occurs when cloud spending reaches 50-75% of cost of revenue. At this level, the savings from private cloud migration can dramatically improve gross margins and, consequently, company valuations.
The time horizon matters significantly in TCO calculations. While public cloud offers advantages for new products and variable workloads, established SaaS applications with predictable usage patterns benefit from private cloud’s cost structure.
Geographic distribution requirements can also favor private cloud, particularly for SaaS companies serving enterprise customers with data residency requirements or those expanding internationally.
Strategic Implementation for PE Portfolio Companies
For private equity firms managing SaaS portfolio companies, infrastructure optimization represents a clear value creation opportunity that becomes more valuable as companies scale.
The most effective approach involves early assessment of each portfolio company’s cloud spending trajectory. Companies approaching $1 million in annual cloud spend should begin evaluating private cloud alternatives, as this threshold often represents the point where optimization efforts justify the transition costs.
Implementing cloud cost tracking and optimization practices across portfolio companies creates consistent management practices and identifies companies ready for infrastructure transitions. Some PE firms establish shared services or preferred vendor relationships to streamline private cloud adoption across their portfolios.
The key insight for PE operating partners is recognizing infrastructure optimization as a financial engineering opportunity rather than just a technical decision. Given that infrastructure costs directly impact gross margins and, consequently, valuations, the ROI on infrastructure optimization efforts can exceed traditional operational improvements.
Building Your Migration Strategy
Successful private cloud migrations require systematic planning and execution. The first step involves comprehensive assessment of current cloud spending, including often-overlooked costs like data egress and premium support charges.
Workload analysis helps identify the best candidates for migration. Applications with steady resource requirements, predictable traffic patterns, and high current cloud costs typically deliver the best results from private cloud migration.
Performance testing validates that applications will meet SLA requirements in the new environment. OpenMetal’s infrastructure allows for comprehensive testing before production migration, reducing the risk of service disruption.
Financial modeling should account for both direct cost savings and indirect benefits like improved performance and reduced operational complexity. The most accurate TCO comparisons include staff time, support costs, and the value of improved predictability in financial planning.
Change management becomes crucial for successful transitions. Teams need training on new platforms and processes, but the investment typically pays dividends through improved operational efficiency and cost control.
Ready to evaluate private cloud for your SaaS portfolio? For PE firms and SaaS leaders looking to control infrastructure costs while maintaining growth trajectories, the TCO advantages of private cloud become compelling at scale. OpenMetal’s hosted private cloud platform eliminates the complexity of hardware management while delivering the cost predictability and performance control that growing SaaS companies need.
Explore how private cloud can optimize your portfolio’s infrastructure costs →
Read More on the OpenMetal Blog



































