What Is Cloud Cost Optimization?
Cloud cost optimization is the practice of efficiently managing the cost of your business’ cloud computing resources. An effective cloud cost optimization strategy ensures that your business gets the best value from its cloud investments. This strategy will find the right balance between performance, cost, compliance, and security for each workload or application your business has in the cloud.
Designing the best cloud cost optimization strategy for your business will require a thorough understanding of the cloud workloads and the ability to predict their future trajectories. This process also requires a familiarity with the complex pricing models of various cloud providers, which in itself can be a dauting task.
Additionally, the individual(s) working on optimizing your cloud cost will need to thoroughly understand your business’ finances (including the cloud budget and expected ROI on cloud expenditures), and an awareness of your engineers’ technical expertise and limitations, among other factors.
Given the intricate nature of cloud environments, effective optimization relies on detailed metrics, analytics, and the use of automated tools. A small-medium size business may do this once a year as they plan their budget for the next year. But larger enterprises may have a team dedicated to this task year-round to ensure that as their cloud usage increases, they continue to find the best value for their investment.
Why Do I Need Cloud Cost Optimization?
Cloud bills have been soaring, and burning significant revenue. Optimizing your cloud cost can significantly impact your business’ profit margin or allow you to purchase additional resources without additional budget.
According to the 2023 Flexera Cloud report, the average business spends 33% of its IT budget on cloud services. They predict that this percentage is expected to increase to 43% by 2025. Now when you consider cloud waste, it’s possible that 28% of your business’ cloud spend is wasted – that’s a significant waste! The practice of cloud optimization plays a crucial role in reducing wasted cloud spend and preventing unnecessary expenditures by pinpointing unused resources and overlooked tools.
Specifically answering the question of “Why do I need to optimize my cloud costs” is tied to your scale. Most companies reach a certain tipping point when cloud expense requires greater oversight. In addition to optimizing in place, most IT leaders consider other cloud deployment models and look specifically at cost tipping points from public cloud to private cloud.
It is important to note that cloud optimization is not solely about reducing costs. An effective cloud cost optimization strategy will involve aligning your business’ expenses with your business goals. Spending more on a cloud service could be justified if it leads to increased revenue or productivity.
Implementing an effective cloud cost optimization strategy will enable your business to effectively manage and control your cloud expenses without compromising performance, ensuring a balance between cost efficiency and achieving business objectives.
Top 10 Strategies For Cloud Cost Optimization
- Understand Your Cloud Bill
The first step to controlling your bill is understanding what your high cost areas are. If you purchased resources for a workload that has significantly grown, you may have fallen in the trap of looking at the cost in parts. Now that you are looking at the bill for all of those instances combined, you’re realizing that it would be significantly more cost effective to move this workload over to a hosted private cloud. Or you may spot inconsistencies and identify idle or wasted resources.
Additionally, for the finance team who are not as intimately acquainted with the fluctuating resource requirements of the IT team, this will allow you to identify trends and patterns over years to be able to predict, within a reasonable margin of error, how many resources you need to budget for. - Identify Wasted Resources (Idle and Unutilized)
Sometimes temporary servers are provisioned but developers or administrators forget to deprovision them after the task is complete. Or they forgot to remove the attached storage. Temporary resources are typically provisioned at on-demand rates, which are elevated, and these charges persist until the resources are deprovisioned. Additionally, some of your instances may be larger than necessary with the anticipation of spikes. It helps to control your infrastructure cost by merging those workloads and then auto-scaling when you have a spike. - Set Budgets
It can be easier to control your bill by setting budgets versus finding ways to cut costs after getting blind-sided by run away bills. It is important for engineering leaders and other executives to come together and set a budget based on project requirements and available financial resources that can be invested into this project. Most providers have a budget system in place, some are more complicated than others to navigate.
With OpenMetal, you pay for the block of resources so leaving your cloud idle won’t affect your bill but there are some variable factors that may alter your bill like egress usage, scaling up, etc. Administrators can set budgets within the dashboard which will prevent users or even auto-scaling from provisioning resources that will go above your budget, but administrators can easily adjust budgets at anytime. - Right-Size Your Resources and Auto Scale When Needed
As mentioned in section two, it’s not uncommon to have resources that need to change size to accommodate spikes. It may be tempting to leave the instances larger to avoid tedious scaling up and down but there are right-size services that can help you automate the process of scaling your instances up and down and help you avoid paying for idle resources. - Save With Reserved and Spot Instances
On-demand instances are flexible and highly available but they come with a significant premium that can easily inflate your infrastructure bill. Reserved and spot instances provide you with instances at significantly lower prices. It may be difficult to plan your need for unpredictable workloads well in advance for reserved instances, and spot instances run the risk of disruption that may be too much of a hassle for the savings. However, some cloud providers like OpenMetal extend fair advance notice to users of spot instances. This makes these instances a practical choice for temporary and unpredictable workloads. If the instance need persists, transitioning to a reserved instance is a seamless option. - Monitor Your Cloud Usage (Cloud Monitoring Tools)
Vigilantly monitoring cloud usage through dedicated cloud monitoring tools can help your businesses optimize your operational costs and ensure efficient resource utilization. Cloud monitoring tools provide real-time insights into various aspects of cloud performance, such as server load, network traffic, and storage usage. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks, forecast capacity needs, and pinpoint opportunities for optimization. Additionally, cloud monitoring tools facilitate the detection of any abnormal activities or security threats, enhancing overall system integrity.
Through proactive monitoring, businesses can make informed decisions, adjust resource allocations, and address issues promptly, contributing to a streamlined and cost-effective cloud infrastructure. Monitoring tools also work with your right-sizing tools to help accurately predict needs before they arrive. Most providers have a dashboard in which you can monitor your cloud usage; OpenMetal uses Datadog which allows users to oversee all layers of their deployments. - Multi-Cloud Solutions
Cloud prices vary based on instance type, size, and vendor. The vendor you choose for each workload will vary based on the instance type you need and the size of your workload.
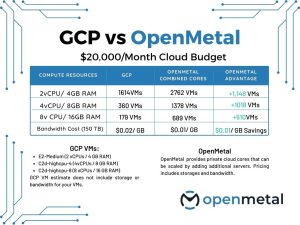
 For small workloads, it’s best to use public cloud instances unless there’s an anticipation that this workload will dramatically increase within three months to the point of needing over 50 instances. For larger workloads it would be cost effective to use a hosted private cloud. The chart on the left compares the resources you can purchase with a budget of $20,000 between a public cloud provider like GCP and a hosted private cloud provider like OpenMetal. With a hosted private cloud, you have significantly more computing resources within the same budget.
For small workloads, it’s best to use public cloud instances unless there’s an anticipation that this workload will dramatically increase within three months to the point of needing over 50 instances. For larger workloads it would be cost effective to use a hosted private cloud. The chart on the left compares the resources you can purchase with a budget of $20,000 between a public cloud provider like GCP and a hosted private cloud provider like OpenMetal. With a hosted private cloud, you have significantly more computing resources within the same budget.
Now, if you have a variety of small workloads you can also run them on different instances on the same cloud. A cost effective multi-cloud strategy will choose the best public instances for your workloads comparing both pricing and performance. But additionally, it will identify when your cloud spend and resource needs are high enough that makes sense to move workloads from public cloud to hosted private cloud. - Use Appropriate Storage Solutions
As with your instances, storage also comes at a price. It’s important to ensure that your storage clusters are adequately sized. In addition to storage size your provider may offer a variety of storage classes, tailored to the frequency of data access. This helps create a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness. Businesses can also control the cost of their cloud storage by implementing lifecycle policies, leveraging compression and deduplication techniques, and utilizing cloud-native database services with built-in optimization features contributing to efficient storage management. - Identify and Minimize Software License Costs
Recognizing and mitigating software license costs helps in fine-tuning cloud expenditure for businesses. Many cloud services charge based on the number of software licenses utilized. Therefore, it is important for organizations to conduct a meticulous inventory of their software assets. By identifying redundant or underutilized licenses, businesses can eliminate unnecessary expenses.
Additionally, opting for open-source alternatives or negotiating flexible licensing agreements with vendors can contribute to substantial savings. Thoughtful handling of software licenses not only helps control costs but also ensures that resources are used wisely. This allows businesses to manage their finances effectively while navigating the complexities of the cloud landscape. - Limit Data Transfer Fees
One of those variable factors in your cloud bill that cannot be fixed is egress. Egress cost also varies across providers. If you are in an industry such as media and entertainment, e-commerce, research and academia, gaming, etc., where egress can be a significant part of your cloud usage, choosing a provider with lower egress costs is imperative. Additionally, businesses can implement several practical strategies to reduce data transfer costs. Businesses can use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and enhance their website and application performance by compressing and caching to lighten data loads. Employing techniques such as data compression and deduplication, along with prioritizing essential data transfers, helps allocate resources wisely.
The right cloud cost strategy for your business will depend on the needs and ability (both financial and technical) of your organization. But using all or a combination of the above will help your business get started building an effective cloud cost optimization strategy to get the most out of your cloud budget.
What are Hosted Private Clouds?
Hosted private clouds are similar to private solutions in the sense that only one cloud is hosted on the servers allocated to your cloud. No one else has workloads on it. This gives your team the root level access to fine tune and customize the cloud as you need. Additionally, hosted private clouds are also similar to public cloud in the sense that you can deploy a production ready cloud in 45 seconds, quickly scale resources by adding or removing servers, and OpenMetal engineers are responsible for maintaining the hardware and updates in your clouds.
OpenMetal’s hosted private cloud begins with a foundational element known as the Cloud Core. The Cloud Core consists of three hosted servers, configured according to your preferred hardware specifications, delivered as a service. This cloud infrastructure harnesses the capabilities of OpenStack and Ceph, encompassing a wide array of services ranging from Compute/VMs and Block Storage to robust software-defined networking and easily deployable Kubernetes clusters. Additionally, it incorporates built-in monitoring tools and is conveniently accessible through a modern portal.
OpenMetal’s hosted private clouds are designed with an API-first approach, making it simple for teams to utilize infrastructure as code. For added convenience, command-line (CLI) and graphical (GUI) interfaces are readily available by default. OpenMetal’s hosted private clouds combine the perks of both traditional and public clouds to give our customers a hassle-free cloud without compromise.
Learn More About Hosted Private Cloud
More on the OpenMetal Blog…

Leveraging On-Demand Private Clouds: A Guide for CTOs
Explore this comprehensive guide on how Chief Technology Officers (CTOs) and technical executives can harness the power of on-demand private clouds for their organizations. In ….Read More

Private Clouds in FinOps: Strategic Insights
ncorporating private clouds into your organization’s FinOps strategy offers numerous strategic advantages, particularly in terms of cost optimization and resource management…Read More

AWS vs GCP: Choosing the Right Cloud Platform
AWS and GCP are leading players in cloud computing, offering a wide range of services and attractive pricing. However, choosing the right platform requires understanding their strengths … Read More
Test Drive
For eligible organizations, individuals, and Open Source Partners, Private Cloud Cores are free to trial. Apply today to qualify.
Subscribe
Join our community! Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest company news, product releases, updates from partners, and more.