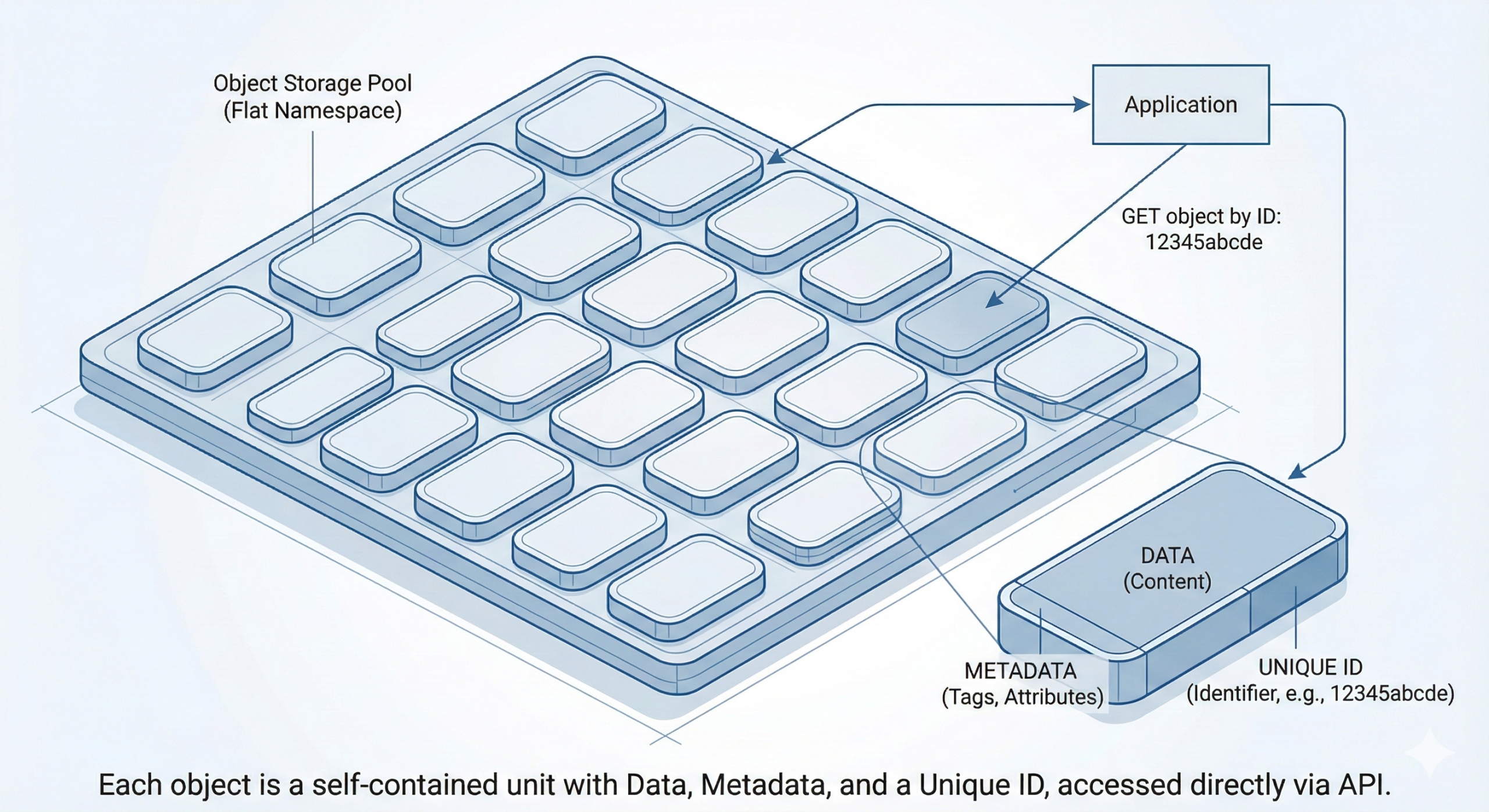
In this article
- Understanding Object Storage
- Ceph: The Unified Storage Platform
- MinIO: The Kubernetes-Native Object Store
- Use Case Comparison
- Performance on OpenMetal Infrastructure
- Cost Considerations
- Making Your Decision
- Getting Started on OpenMetal
- Wrapping Up: Choosing Between Ceph and MinIO
Object storage has become a cornerstone of modern cloud infrastructure, handling everything from backups to media files to massive data lakes. At OpenMetal, we support both Ceph and MinIO as powerful object storage solutions. Each brings different strengths to the table, and understanding these differences will help you make the right choice for your infrastructure.
Understanding Object Storage
Object storage works differently than traditional file or block storage. Instead of organizing data in hierarchical directories or fixed-size blocks, it manages data as discrete objects. Each object includes the data itself, custom metadata, and a unique identifier. This approach enables massive scalability and works particularly well for cloud-native applications, backup systems, media repositories, and data lakes.
Ceph: The Unified Storage Platform
What is Ceph?
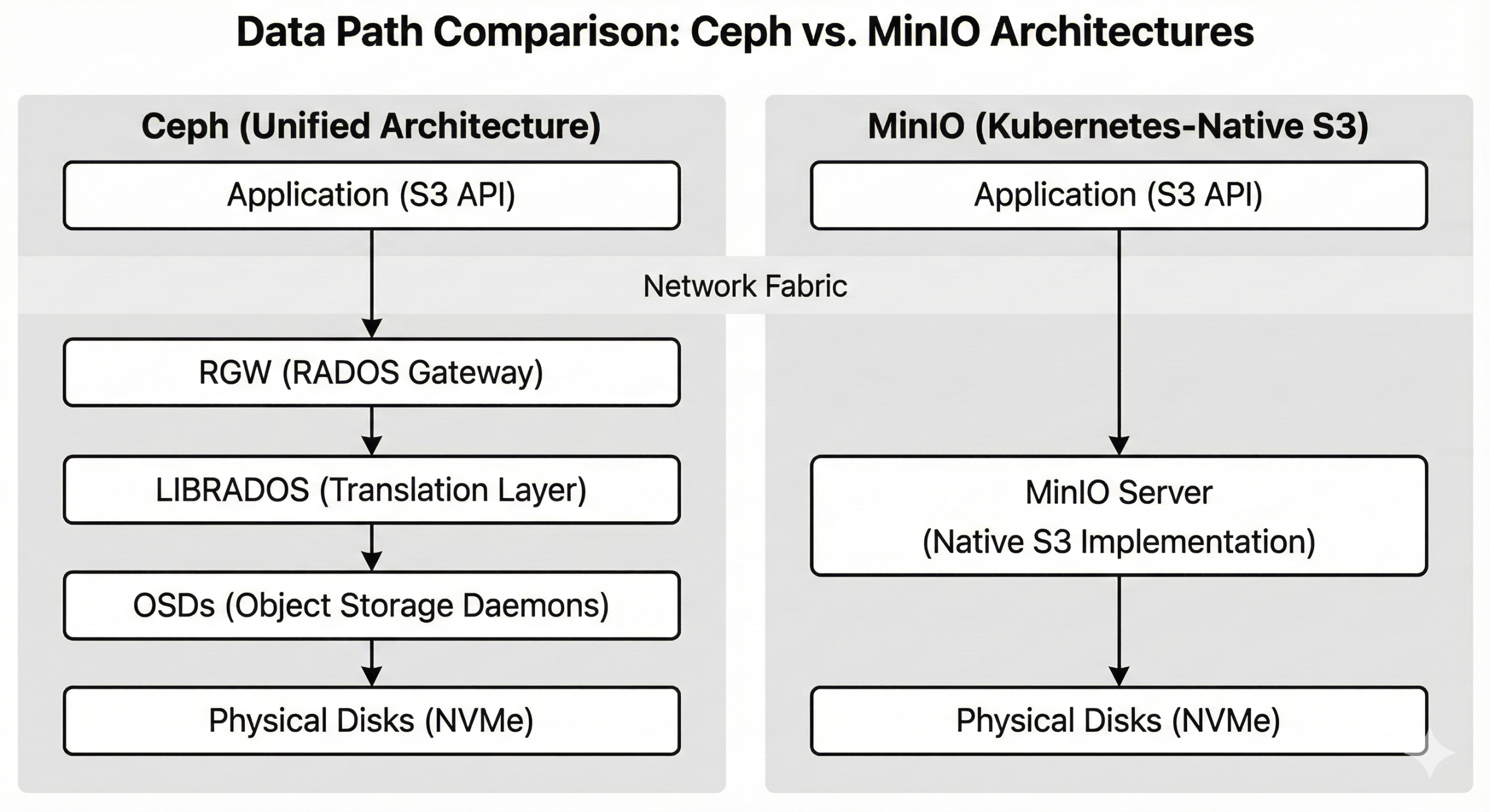
Ceph is an open source, software-defined storage platform that handles object, block, and file storage from a single cluster. Originally developed in 2006 and now part of the Linux Foundation, Ceph has grown into an enterprise-grade solution deployed by organizations worldwide.
Ceph’s Architecture
Ceph’s architecture includes several key components:
- RADOS (Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Store): The foundation layer handling data distribution, replication, and recovery
- RADOS Gateway (RGW): Provides S3 and Swift-compatible object storage interfaces
- RBD (RADOS Block Device): Delivers block storage for virtual machines and containers
- CephFS: Offers POSIX-compliant distributed file system capabilities
This unified architecture means Ceph can serve multiple storage needs from one cluster, which simplifies infrastructure management considerably.
Key Advantages of Ceph
Unified Storage Platform: Ceph’s ability to provide object, block, and file storage from the same cluster cuts down on infrastructure complexity. When running OpenStack on OpenMetal, Ceph can simultaneously serve as the backend for Nova (compute), Cinder (block storage), Glance (image storage), and provide S3-compatible object storage through RGW. Instead of managing three separate storage systems, you’re managing one.
Self-Healing and Resilience: Ceph automatically detects and recovers from hardware failures. The CRUSH algorithm redistributes data across the cluster when components fail, maintaining data availability without manual intervention. For large-scale deployments where hardware failures aren’t a question of “if” but “when,” this self-healing capability saves significant operational headaches.
Flexible Data Protection: Ceph supports both replication and erasure coding for data protection. Replication (2x or 3x) provides faster performance and simpler operation, while erasure coding delivers storage efficiency comparable to RAID schemes but distributed across the cluster. For large datasets, erasure coding can reduce storage overhead from 200% (with 3x replication) to as low as 50%, depending on the erasure coding scheme chosen. That’s real cost savings when you’re dealing with petabytes of data.
Deep OpenStack Integration: As a native OpenStack storage backend, Ceph integrates seamlessly with OpenStack services. On OpenMetal’s platform, this integration comes pre-configured and optimized, so you can start taking advantage of Ceph’s capabilities immediately after deploying your private cloud.
Enterprise Maturity: With over 15 years of development and production deployments at massive scale (some clusters exceeding 100+ petabytes), Ceph has proven itself for mission-critical workloads. The active community and commercial support options provide confidence for long-term deployments.
Ceph Performance Considerations
Ceph’s performance depends heavily on the underlying hardware and cluster configuration. On OpenMetal’s NVMe-based infrastructure, Ceph delivers excellent performance for both object and block storage workloads. However, Ceph’s distributed nature means that object storage operations traverse more layers than simpler object storage systems, which can impact latency for small object operations.
For optimal performance, Ceph benefits from:
- Fast storage media (NVMe SSDs, available on all OpenMetal cloud cores)
- High-bandwidth networking (OpenMetal provides dual 10Gbps per server)
- Sufficient CPU resources for erasure coding and encryption operations
- Proper tuning of CRUSH maps and placement groups
MinIO: The Kubernetes-Native Object Store
What is MinIO?
MinIO is a high-performance, Kubernetes-native object storage system built specifically for cloud-native workloads. Released in 2015, MinIO focuses exclusively on object storage, offering S3 API compatibility with impressive performance and operational simplicity.
MinIO’s Architecture
MinIO’s architecture is notably simpler than Ceph’s:
- Erasure Coding: Built-in data protection using Reed-Solomon codes
- Server Pools: Groups of servers that expand capacity
- Distributed Design: Scales horizontally across nodes with no single point of failure
- Native S3 API: Direct implementation of Amazon S3 API without translation layers
Key Advantages of MinIO
Exceptional Performance: MinIO is engineered for speed. Its streamlined architecture and native S3 implementation often deliver superior throughput and lower latency compared to Ceph’s RGW, particularly for small to medium-sized objects. MinIO has demonstrated over 325 GB/s on 32 nodes with standard hardware, and this performance scales linearly as you add nodes.
Simplicity and Ease of Deployment: MinIO’s single-purpose design makes it significantly simpler to deploy and operate than Ceph. A basic MinIO deployment can be running in minutes with a single command or Helm chart. This simplicity extends to operations; MinIO requires less tuning and specialized expertise to maintain optimal performance.
Kubernetes-Native: MinIO is designed for Kubernetes environments and integrates with cloud-native workflows. The MinIO Operator for Kubernetes handles deployment, scaling, and lifecycle management, making it an excellent choice for containerized workloads. OpenMetal’s platform provides an ideal foundation for running MinIO in Kubernetes, with the underlying infrastructure already optimized for container workloads.
Active-Active Replication: MinIO supports multi-site active-active replication, allowing geographic distribution with local read and write access at each site. This capability is valuable for globally distributed applications and disaster recovery scenarios.
Resource Efficiency: MinIO’s focused design results in lower CPU and memory overhead compared to Ceph. For pure object storage workloads, this efficiency translates to cost savings and the ability to achieve higher performance with less infrastructure.
Modern Feature Set: MinIO includes advanced capabilities like bucket versioning, object locking (WORM), lifecycle management, encryption (at rest and in transit), and comprehensive IAM policies—all implemented with performance in mind.
MinIO Performance Considerations
MinIO excels at object storage performance but requires proper configuration for optimal results:
- Server Sizing: MinIO recommends specific drive configurations (4, 8, or 16 drives per server) for optimal erasure coding efficiency
- Network Bandwidth: High-bandwidth networking (10Gbps or higher) is necessary for distributed deployments
- Drive Homogeneity: All drives in a MinIO deployment should be identical for consistent performance
- Proper Erasure Coding: Choosing the right EC:N ratio balances performance, capacity efficiency, and fault tolerance
On OpenMetal’s infrastructure, MinIO can leverage the high-performance NVMe storage and 10Gbps networking to deliver exceptional object storage performance.
Use Case Comparison
When to Choose Ceph
- Unified Storage Requirements
If your infrastructure needs object, block, and file storage, Ceph’s unified platform eliminates the complexity of managing separate storage systems. This is particularly valuable in OpenStack environments where multiple storage types are required.
Example: A private cloud deployment serving multiple departments needs block storage for virtual machines, object storage for backups and user files, and shared file storage for collaboration. A single Ceph cluster can serve all these needs efficiently.
- OpenStack Deployments
For OpenStack private clouds on OpenMetal, Ceph provides native integration with deeper capabilities than external object storage solutions. The tight integration reduces latency for operations like VM image management and volume operations.
Example: An organization running OpenStack on OpenMetal can use Ceph for all backend storage, with pre-configured integration delivering optimal performance and simplified operations.
- Large-Scale Storage (Multi-PB)
Ceph’s maturity at massive scale makes it ideal for petabyte-scale deployments. Organizations managing large media repositories, scientific datasets, or long-term archives benefit from Ceph’s proven scalability.
Example: A research institution storing petabytes of scientific data can use Ceph’s erasure coding to achieve 50% storage efficiency while maintaining high availability and performance.
- Complex Data Protection Requirements
When you need fine-grained control over data protection strategies—mixing replication for hot data and erasure coding for cold data, for instance—Ceph’s flexibility becomes an advantage.
Example: A video streaming platform uses 2x replication for frequently accessed content (fast performance) and 5+2 erasure coding for archived content (storage efficiency), all within the same Ceph cluster.
When to Choose MinIO
- Kubernetes-Native Applications
For applications deployed on Kubernetes, MinIO’s native integration provides the most seamless object storage experience. The MinIO Operator simplifies deployment and lifecycle management.
Example: A microservices application running on Kubernetes needs scalable object storage for user-generated content. MinIO deploys alongside the application with the MinIO Operator, providing S3-compatible storage with minimal operational overhead.
- Performance-Critical Object Storage
When object storage performance is paramount and you don’t need block or file storage capabilities, MinIO’s focused design delivers superior throughput and latency.
Example: A machine learning pipeline processes large datasets stored in object storage. MinIO’s high-performance design accelerates data loading, reducing training time and infrastructure costs.
- Simplified Operations
Organizations with limited storage expertise or those seeking to minimize operational complexity benefit from MinIO’s straightforward architecture and management.
Example: A growing SaaS company needs reliable object storage without dedicating staff to storage specialization. MinIO’s simplicity allows the team to deploy and maintain object storage with minimal effort.
- Multi-Site Deployments
MinIO’s active-active replication enables sophisticated multi-site architectures with local read/write access at each location.
Example: A global application serves users across multiple continents. MinIO’s site replication helps users access data with low latency while maintaining consistency across regions.
- Pure Object Storage Needs
When your infrastructure only requires object storage (no block or file storage), MinIO’s focused design provides a more efficient and performant solution than Ceph.
Example: A backup service needs massive-scale object storage for customer backups. MinIO’s S3 compatibility provides seamless integration with backup software, while its performance handles high-volume data ingestion.
Performance on OpenMetal Infrastructure
Both Ceph and MinIO benefit from OpenMetal’s high-performance infrastructure:
Hardware Advantages
NVMe Storage: All OpenMetal cloud cores include NVMe SSDs (Micron 7450 or 7500 MAX series), providing the high-IOPS, low-latency storage that both Ceph and MinIO need for optimal performance.
10Gbps Networking: Dual 10Gbps network interfaces (20Gbps total) per server keep storage traffic flowing smoothly, which is critical for distributed storage performance.
Modern CPUs: OpenMetal’s Xeon processors provide the compute power needed for encryption and erasure coding operations without impacting storage performance.
Deployment Flexibility
OpenMetal’s architecture supports various deployment strategies:
Hyper-Converged: Run storage and compute on the same nodes, ideal for smaller deployments or when the workload pattern allows efficient resource sharing.
Converged: Add additional storage-focused nodes to an existing cluster, balancing compute and storage resources independently.
Storage Clusters: Deploy dedicated Ceph or MinIO clusters (minimum 3 nodes for high availability), optimal for large-scale storage requirements or when complete separation of storage and compute is desired.
Scaling Patterns
Both solutions scale effectively on OpenMetal:
Ceph: Add converged nodes to expand both capacity and performance. OpenMetal’s infrastructure automation provisions new nodes in minutes, and Ceph automatically rebalances data across the expanded cluster.
MinIO: Add server pools to increase capacity and throughput. MinIO’s erasure coding spans the new servers, immediately contributing to both performance and capacity.
Cost Considerations
Storage costs extend beyond the base hardware pricing. Consider the total cost of ownership:
Capacity Efficiency
Ceph:
- 2x replication: 50% efficiency (2TB usable from 4TB raw)
- 3x replication: 33% efficiency (3TB usable from 9TB raw)
- Erasure coding (4+2): 67% efficiency (4TB usable from 6TB raw)
- Erasure coding (8+3): 73% efficiency (8TB usable from 11TB raw)
MinIO:
- Typical erasure coding (EC:4): 67% efficiency
- Erasure coding (EC:2): 50% efficiency
- Erasure coding (EC:8): 80% efficiency
Erasure coding provides significant capacity advantages for large datasets, though it requires additional CPU for encoding/decoding operations.
Operational Costs
Ceph: Requires more specialized expertise for tuning and troubleshooting, potentially increasing operational costs.
MinIO: Lower operational overhead due to simpler architecture, reducing the expertise required for day-to-day operations.
Performance vs. Cost Trade-offs
Higher performance often requires more resources:
- More NVMe drives improve IOPS and throughput but increase hardware costs
- Higher replication factors increase resilience but reduce capacity efficiency
- Lower CPU allocation (for erasure coding) can impact performance under load
OpenMetal’s flexible deployment options allow you to optimize this balance for your specific requirements and budget.
Making Your Decision
Choosing between Ceph and MinIO depends on your specific infrastructure needs:
Choose Ceph when:
- You need unified storage (object, block, and file)
- Running OpenStack and want native integration
- Managing multi-petabyte scale storage
- Requiring sophisticated data protection strategies
- Your team has or can develop Ceph expertise
Choose MinIO when:
- Object storage is your primary requirement
- Running Kubernetes-native workloads
- Performance and simplicity are priorities
- Need multi-site active-active replication
- Want minimal operational overhead
Getting Started on OpenMetal
OpenMetal’s platform provides a solid foundation for both Ceph and MinIO:
Ceph on OpenMetal
OpenMetal’s Private Cloud Cores include Ceph pre-configured and integrated with OpenStack. Your Ceph cluster is ready to use immediately after cloud deployment, with:
- Optimized configuration for OpenMetal hardware
- Pre-integrated with OpenStack services
- Object storage (S3/Swift) ready to use via RADOS Gateway
- Support for expanding with additional converged or storage nodes
MinIO on OpenMetal
Deploying MinIO on OpenMetal is straightforward:
- Provision nodes: Deploy standard or large compute nodes for your MinIO cluster
- Install MinIO: Use the MinIO Operator for Kubernetes or direct installation
- Configure erasure coding: Set up appropriate EC:N ratio for your use case
- Connect applications: Point applications to MinIO’s S3-compatible endpoint
OpenMetal’s support team can assist with architecture recommendations and deployment best practices for both platforms.
Wrapping Up: Choosing Between Ceph and MinIO
 Both Ceph and MinIO are excellent object storage solutions, each with advantages. Ceph’s unified storage platform and deep OpenStack integration make it ideal for private cloud deployments with diverse storage needs. MinIO’s performance and Kubernetes-native design excel for cloud-native applications with focused object storage requirements.
Both Ceph and MinIO are excellent object storage solutions, each with advantages. Ceph’s unified storage platform and deep OpenStack integration make it ideal for private cloud deployments with diverse storage needs. MinIO’s performance and Kubernetes-native design excel for cloud-native applications with focused object storage requirements.
OpenMetal’s high-performance infrastructure and flexible deployment options support both solutions effectively. Whether you choose Ceph, MinIO, or deploy both in a complementary architecture, OpenMetal provides the foundation for reliable, performant object storage.
Ready to explore object storage on OpenMetal? Contact our team to discuss your specific requirements and get started with a proof of concept deployment tailored to your needs.
Schedule a Consultation
Get a deeper assessment and discuss your unique requirements.
Read More on the OpenMetal Blog