Introduction
Although the Horizon dashboard provided in OpenStack is useful for most tasks, infrastructure automation tools like Terraform exist to allow you to create your infrastructure as code. This allows your infra teams to follow standard development flows and implement CI/CD to fully automate your cloud. When you complete this guide (or before) you may also interested in Terraform Automation in our Operator’s Manual.
In this guide, you will configure Terraform to leverage OpenStack with a generated clouds.yaml.
When you’re finished, you’ll be able to automate your cloud like a pro!
Prerequisites
Before you begin this guide you’ll need the following:
- A local machine or jumpstation (control node) with Terraform downloaded and installed.
- An OpenStack user with access to a project. If you are the admin on an OpenMetal Hosted Private Cloud, check out our OpenStack guides so you can create a project specifically for this.
- A text editor or IDE
Step 1 — Generate a clouds.yml from OpenStack
First step is to navigate to the correct area to generate the clouds.yaml.
Once logged into the Horizon dashboard on the top left navigation area, click on the API Access tab.
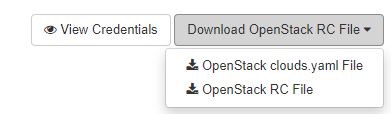
Next select the dropdown on the “Download OpenStack RC File” and select the option to “OpenStack clouds.yaml file”
The contents of the clouds.yaml should look like the following below. If you want a completely seamless experience you will need to add your password to the auth section.
clouds:
flex_metal:
auth:
auth_url: https://openstack-cluster.url:5000
username: "docs"
project_id: 0cbe14b0db11426c8413d9f4eaa13311
project_name: "docs"
user_domain_name: "Default"
region_name: "lax"
interface: "public"
identity_api_version: 3
Now that we have the clouds.yaml we can configure terraform to use it.
Step 2 — Configure Terraform with clouds.yaml
First, place the clouds.yaml into the current working directory of your Terraform file. It can also be placed in ~/.config/openstack or /etc/openstack.
Next we will modify the OpenStack provider in Terraform to specify the OpenStack cluster in our clouds.yaml. In our example our cluster is named flex_metal be sure to use whichever cluster name that is specified in your file.
provider "openstack" {
cloud = "flex_metal"
}
Once that is modified correctly, you should be able to run terraform init to finish the setup.
root@crees-pc: ~/terraform/openstack # terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
Step 3 — Automate your OpenStack cloud!
Now that everything is configured, you should be able to run your Terraform modules or create your own and automate against your OpenStack cluster. Some of the next tasks you can do is to edit your clouds.yaml to add more cluster, and automate against multiple cloud infrastructures all at once!
If you haven’t worked with OpenStack recently, we invite you to try our new Hosted Private Cloud. It is on-demand and billed by the hour. Combine the power of on demand OpenStack and Terraform to create massively scaled deployments with ease. For more information, check out Terraform Automation in our Operators Manual.



































